- Mon - Sat 10:00 am - 08:00 pm |
Sunday 10:00 am - 01:00 pm - +(91) 9554015920
- drpaulphysiotherapy@gmail.com
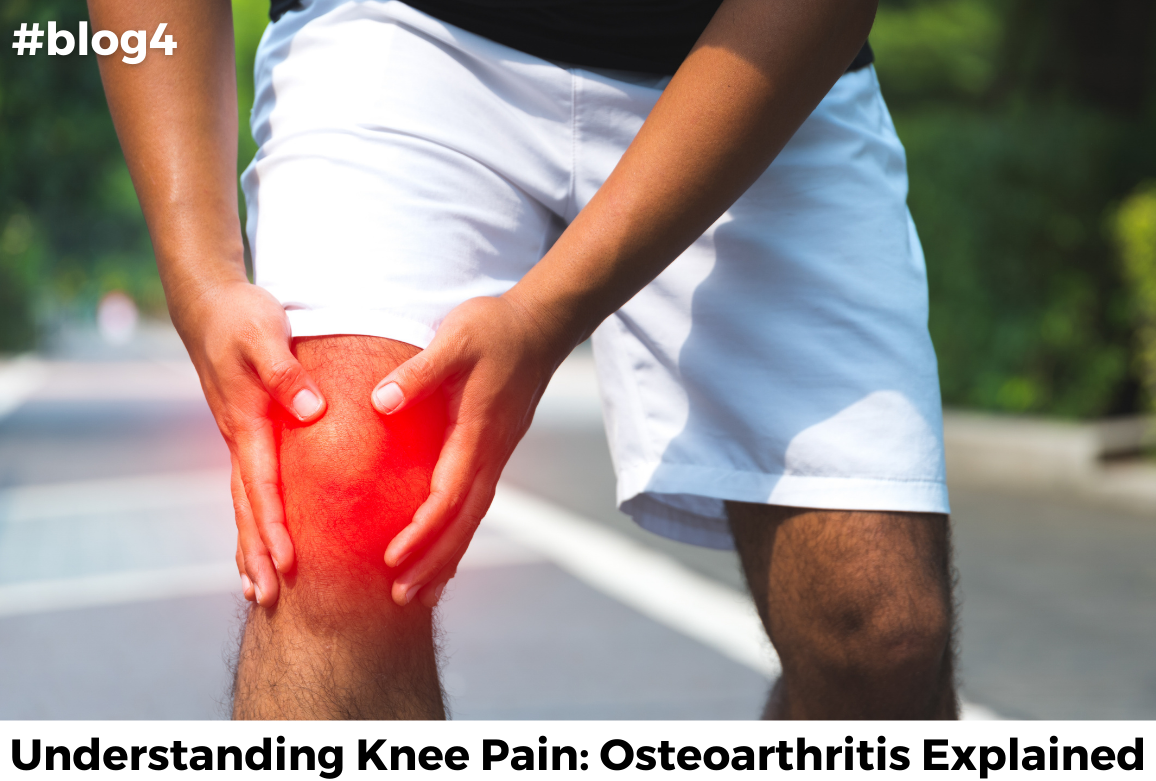
Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition affecting millions worldwide. This condition occurs when the protective cartilage in the knee joint wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis
Persistent knee pain, especially during activities or after periods of rest
Swelling and tenderness around the knee joint
Stiffness, making it difficult to fully bend or straighten the knee
A feeling of weakness or instability in the knee
Several factors contribute to the development of knee osteoarthritis:
1.Age : The risk of knee osteoarthritis increases with age, as cartilage naturally
deteriorates over time.
2.Obesity : Excess weight puts added stress on knee joints, accelerating cartilage
breakdown.
3.Previous Injury : Knee injuries or trauma can increase the likelihood of osteoarthritis
later in life.
4.Genetics : Family history of osteoarthritis can predispose individuals to the condition.
While knee osteoarthritis cannot be cured, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
1. Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and corticosteroid injections can
alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
2.Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises and stretches can improve joint function
and mobility.
3.Lifestyle Changes: Weight management and low-impact exercise can reduce stress
on the knees.
4.Surgery:In severe cases, surgical interventions like knee replacement may be
recommended.
1.Stay Active: Engage in low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to keep joints
flexible.
2.Manage Weight: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on knee joints.
3.Use Assistive Devices : Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on knee joints.
1. Consistent Exercise : Following a tailored exercise regimen prescribed by a
physical therapist.
2.Pain Management: Continuing medications or alternative therapies as
recommended by healthcare providers.
3.Patience : Consider using braces, canes, or shoe inserts to support
the knee and improve mobility.
4.Follow Treatment Plan:: Adhere to prescribed medications and therapies
recommended by healthcare providers.
In conclusion, knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects many individuals, particularly as they age. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to manage knee osteoarthritis effectively and maintain an active lifestyle.